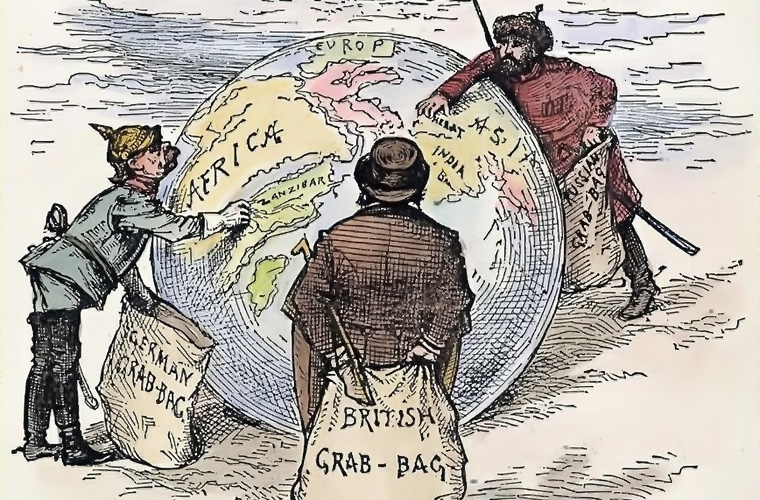
European imperialism refers to the period of European history from the 16th to the 20th centuries when European powers such as Spain, Portugal, Great Britain, France, Belgium, Italy, and Germany established colonies and empires in various parts of the world. This period saw the spread of European influence and control over much of the world, including Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
European imperialism was driven by a combination of economic, political, and cultural factors. European powers sought to expand their markets for goods and resources, acquire strategic military and naval bases, and spread their political and cultural influence. European imperialism had a profound impact on the world, both positive and negative.
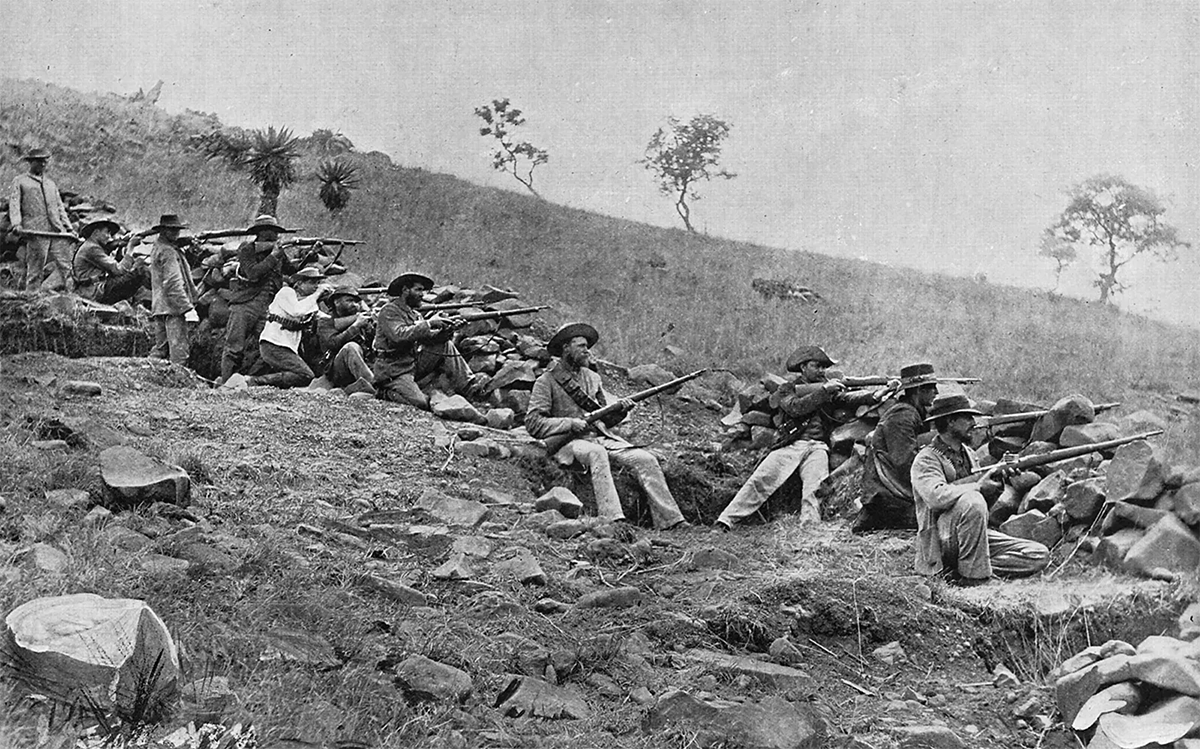

Some of the positive effects of European imperialism include the introduction of new technologies and medicines, improvements in infrastructure such as roads and railways, and the establishment of a global economy. However, the negative effects of European imperialism were far more significant. These included the exploitation of natural resources and human labor, the destruction of local economies and cultures, the suppression of indigenous peoples, and the creation of racial and ethnic hierarchies.
European imperialism was also a major factor in the global conflicts of the 20th century, including World War I and II. The legacy of European imperialism can still be seen today in the political, economic, and cultural structures of many countries around the world.