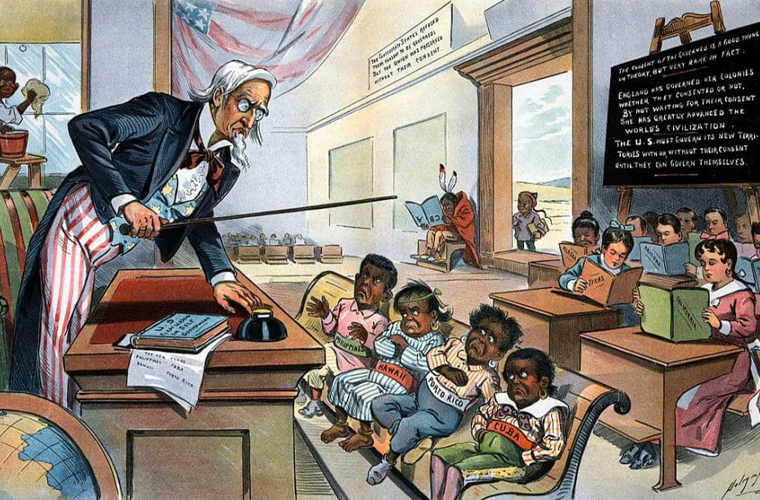
Imperialism is a complex and multifaceted concept that has been practiced throughout history by various empires and nations. At its core, imperialism is the extension of a country’s power and influence beyond its borders, often with the aim of acquiring new territories, resources, or markets.
Historically, imperialism has taken many different forms. One of the most common forms of imperialism was colonization, where a powerful country would establish settlements or take over existing territories in other parts of the world. This often involved the subjugation of the local population and the exploitation of their resources, such as gold, silver, spices, or other valuable commodities. Colonization was often justified by claims of “civilizing” or “modernizing” the colonized peoples, although in reality it often led to the displacement of indigenous populations, the suppression of local cultures, and the imposition of the colonizer’s values and institutions.
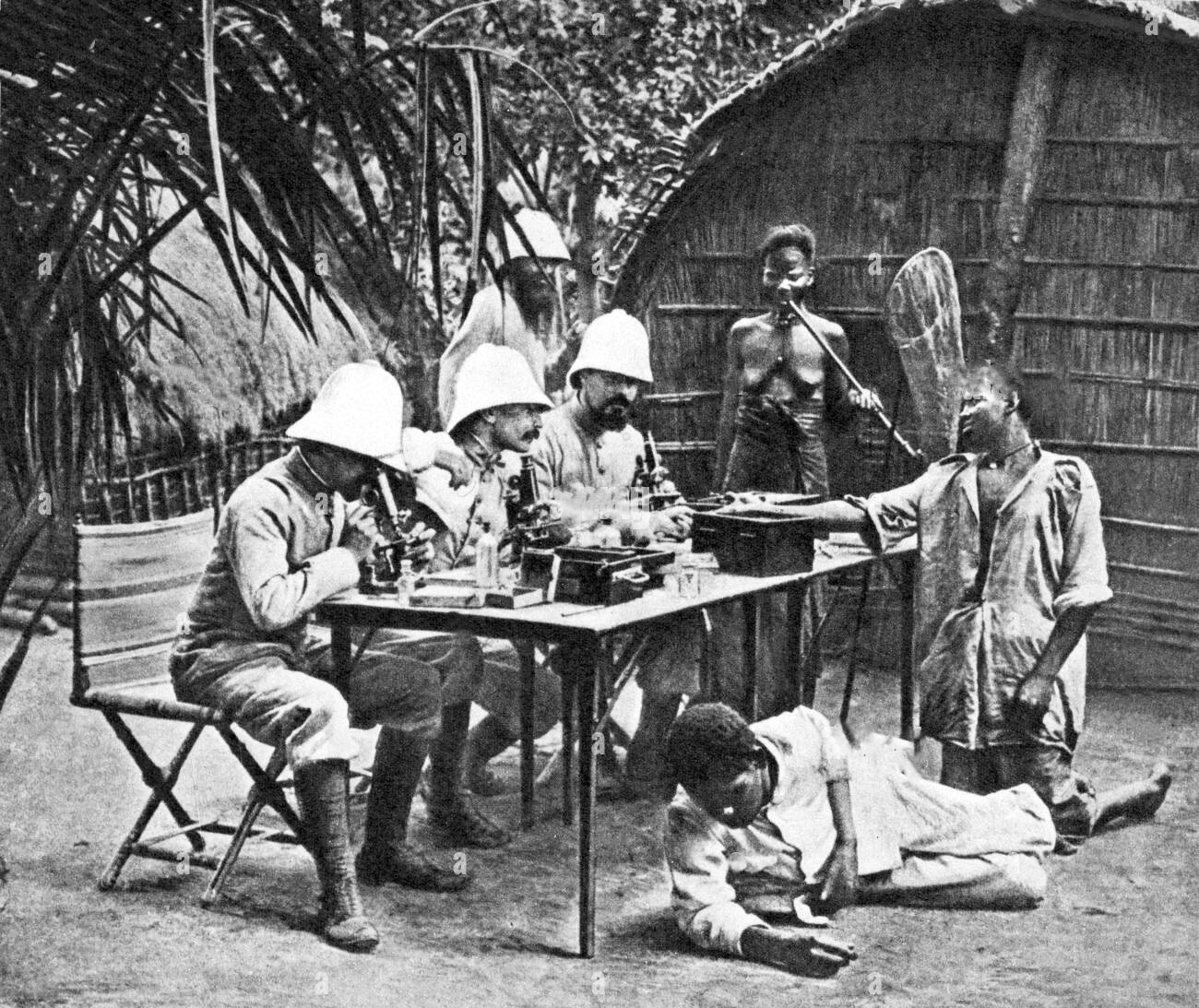

Another form of imperialism is economic imperialism, where a country seeks to dominate other nations through trade and investment policies. This can involve the creation of unequal trade relationships, where the dominant country exports goods and services to the weaker country while importing cheap raw materials and labor. Economic imperialism can also involve the establishment of monopolies or cartels that control the production and distribution of key resources or goods, often to the detriment of smaller, less powerful countries.
Imperialism can also take the form of political or military domination. In these cases, a powerful country may use its military or diplomatic power to exert control over weaker nations, often with the aim of expanding its own territory or influence. This can involve the use of military force, the establishment of puppet governments, or the imposition of political or economic sanctions.
Imperialism has been a source of both conflict and cooperation throughout history. While imperialist policies have often led to the exploitation and suffering of colonized peoples, they have also been responsible for spreading ideas, technologies, and institutions across borders, and for fostering cultural exchange and interdependence. The legacy of imperialism continues to shape global relations today, as many countries continue to struggle with the consequences of past colonialism and economic domination.